Hand surgery is a super specialty that deals with the upper extremity, from hand to shoulder. It is an amazing field that incorporates techniques from orthopaedics, plastic surgery, and general surgery to neurosurgery, vascular, and microvascular surgery. The dimension of hand surgery includes reconstruction of acute trauma, hand fracture fixation and reconstruction, tendon repairs and transfers, post traumatic reconstruction of hand, arthroscopy of wrist and hand, arthroplasty of joints around the hand, wrist, and elbo

w, congenital defect of upper limb, rheumatoid deformities, cerebral palsy, and tetraplegic hands. It also includes microsurgical reattachment of amputated digits and limbs, microsurgical reconstruction of soft tissues, and bone and nerve reconstruction.
Hand surgeons are orthopedic, plastic, or general surgeons who have received specialized training in hand surgery. As of now, only a handful of surgeons in Nepal are trained in hand surgery. Most of them often practice individually in their primary specialty as a generalist orthopedic, plastic, or reconstructive surgeon. Furthermore, after surgical management, the injured hand needs a long time to rehabilitate, and there are very few rehabilitation therapists for this purpose. In addition, most tertiary and quaternary centers do not have set-ups for hand surgery. As a result, most hand injuries often lead to disabilities or amputations, when a majority of them could be salvaged and made functional. cerebral palsy, and tetraplegic hands. It also includes microsurgical reattachment of amputated digits and limbs, microsurgical reconstruction of soft tissues, and bone and nerve reconstruction.
Hand surgeons are orthopedic, plastic, or general surgeons who have received specialized training in hand surgery. As of now, only a handful of surgeons in Nepal are trained in hand surgery. Most of them often practice individually in their primary specialty as a generalist orthopedic, plastic, or reconstructive surgeon. Furthermore, after surgical management, the injured hand needs a long time to rehabilitate, and there are very few rehabilitation therapists for this purpose. In addition, most tertiary and quaternary centers do not have set-ups for hand surgery. As a result, most hand injuries often lead to disabilities or amputations, when a majority of them could be salvaged and made functional.
Why do we need hand surgery?
Hand is crucial in performing all the activities of daily living, from brushing, feeding, and clothing to toileting. It is used for sensation, communication, expressions, and also for cosmesis. Hand is a very specialized part of the body that has a very integrated anatomy. Every tissue (bone, ligaments, tendons, vessels, nerves) needs specialized consideration, requiring orthopedic, plastic/reconstructive, and microsurgery expertise. It needs a long therapy and rehabilitation program synchronized between the surgeon and the therapist for a successful outcome. That’s why hand surgery has developed as a separate specialty in many parts of the world. Countries like Singapore, Sweden, and Finland have separate residency programs in hand surgery, where the residents are trained to become hand surgeons in five to six years.
Hand injuries are very common and ever increasing in number in Nepal. Hand injuries are, by and large, due to road traffic accidents, occupational injuries, farmyard injuries, domestic injuries, etc. As road traffic accidents is becoming epidemic, so is the number of trauma cases. While exact statistics on hand injuries in our country is not available, we did do a cross-sectional study from the computer database of patients presented to the emergency department of a tertiary trauma care center since the last 10 years (2005-2015). The paper was published in 2019 in the Nepal Health Research Council journal. There were 2899 patients with hand and wrist injuries, which accounted for 7.48% of total orthopedic registrations and 4.19% of total emergency registrations. We believe this number is still underrated, as minor hand injuries may not have been recorded or identified in cases of polytraumas or multiple traumas. The table above shows the breakdown of the most common conditions of hand injuries presented during the duration.
do a cross-sectional study from the computer database of patients presented to the emergency department of a tertiary trauma care center since the last 10 years (2005-2015). The paper was published in 2019 in the Nepal Health Research Council journal. There were 2899 patients with hand and wrist injuries, which accounted for 7.48% of total orthopedic registrations and 4.19% of total emergency registrations. We believe this number is still underrated, as minor hand injuries may not have been recorded or identified in cases of polytraumas or multiple traumas. The table above shows the breakdown of the most common conditions of hand injuries presented during the duration.
Hand injury has major influence on the quality of life, if not treated promptly and adequately. Suboptimal management of these injuries can result in persistent pain, excessive tenderness, abnormal sensation, disfigurement, joint stiffness, and reduced grip strength.
Treatment of hand injury is important socially and economically. Often, the injured patient is the breadwinner of the family. Their injury and subsequent under-treatment or non-treatment affects their whole family, and has a ripple effect in the industries they work in. As the concept of worker’s compensation and medical insurance is not available in our country, it is imperative that the patient gets the most appropriate treatment in the first place.
In a paper published in JBJS 2012, de Putter et al. (see table below) outline the economic impact of hand and wrist injuries in a population-based study. The healthcare cost for hand and wrist injuries is second to hip fractures. Interestingly, the overall cost (healthcare and productivity) is the highest with hand and wrist injuries. This is because the overall productivity cost is highest in hand and wrist injuries, as these injuries happen mostly to working people of productive age group. What is striking is that, hand and wrist injuries are very common, and these injuries cause long absenteeism from work because of long-term rehabilitation. We can imagine that hand injuries would be similar in case of Nepal, too. In light of this, this study highlights the importance of hand surgery service for a developing nation like ours.
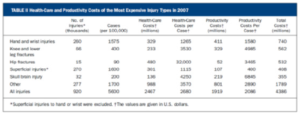
Reference: de Putter et al. JBJS, 2012
 Medicosnext
Medicosnext




